2017.10.05 |
Publications | 臨床 |
 Impact of combined lipid lowering and blood pressure control on coronary plaque: myocardial ischemia treated by percutaneous coronary intervention and plaque regression by lipid lowering and blood pressure controlling assessed by intravascular ultrasonography (MILLION) study
Impact of combined lipid lowering and blood pressure control on coronary plaque: myocardial ischemia treated by percutaneous coronary intervention and plaque regression by lipid lowering and blood pressure controlling assessed by intravascular ultrasonography (MILLION) study
Kawashiri MA, Sakata K, Hayashi K, Gamou T, Kanaya H, Miwa K, Ueda K, Higashikata T, Mizuno S, Michishita I, Namura M, Nitta Y, Katsuda S, Okeie K, Hirase H, Tada H, Uchiyama K, Konno T, Ino H, Nagase K, Yamagishi M; Behalf of the MILLION Study Group.
Heart Vessels. 2017 May;32(5):539-548. 
Impact Factor (2016): 3.434
MILLION試験は冠動脈疾患を有する高血圧・高コレステロール血症合併日本人患者を対象に、LDL-Cと血圧を同時にコントロールすることで、冠動脈プラークの進展抑制・退縮作用をIVUS(血管内超音波)を用いて検証した初めての試験です。当教室が北陸三県を中心とした多施設共同無作為前向き試験として実施しました。

アムロジピンとアトルバスタチンの併用により、標準治療群、積極的治療群ともに有意に冠動脈プラーク体積は有意に減少することを確認しました。
Abstract
The aim of the study was to elucidate the aggressive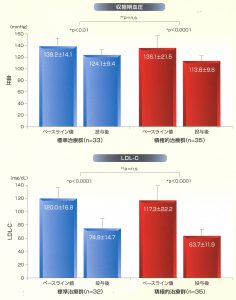 reduction of both low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and blood pressure (BP) reduced coronary atherosclerotic plaque volume compared with a standard treatment of LDL-C and BP in Japanese patients with coronary artery disease (CAD). This study is a prospective, randomized, and open-labelled with a blind-endpoint evaluation study. A total of 97 patients (81 men, mean age 62.0 ± 9.6) with CAD undergoing intravascular ultrasonography (IVUS)-guided percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) were randomized, and 68 patients had IVUS examinations at baseline and at 18-24 months follow-up. Patients were randomly assigned to standard or aggressive strategies targeting LDL-C and a BP of 100 mg/dL and 140/90 mmHg vs. 70 mg/dL and 120/70 mmHg, respectively. The primary endpoint was the percent change in coronary plaque volume. Both standard and aggressive strategies succeeded to achieve target levels of LDL-C and BP; 74.9 ± 14.7 vs. 63.7 ± 11.9 mg/dL (NS) and 124.1 ± 9.4/75.8 ± 7.7 vs. 113.6 ± 9.6/65.8 ± 9.4 mmHg (systolic BP; NS, diastolic BP; p < 0.05), respectively. Both groups showed a significant reduction in the coronary plaque volume of -9.4 ± 10.7% and -8.7 ± 8.6% (NS) in standard and aggressive therapies, respectively. Both standard and aggressive intervention significantly regressed coronary plaque volume by the same degree, suggesting the importance of simultaneous reductions of LDL-C and BP for prevention of CAD.
reduction of both low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and blood pressure (BP) reduced coronary atherosclerotic plaque volume compared with a standard treatment of LDL-C and BP in Japanese patients with coronary artery disease (CAD). This study is a prospective, randomized, and open-labelled with a blind-endpoint evaluation study. A total of 97 patients (81 men, mean age 62.0 ± 9.6) with CAD undergoing intravascular ultrasonography (IVUS)-guided percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) were randomized, and 68 patients had IVUS examinations at baseline and at 18-24 months follow-up. Patients were randomly assigned to standard or aggressive strategies targeting LDL-C and a BP of 100 mg/dL and 140/90 mmHg vs. 70 mg/dL and 120/70 mmHg, respectively. The primary endpoint was the percent change in coronary plaque volume. Both standard and aggressive strategies succeeded to achieve target levels of LDL-C and BP; 74.9 ± 14.7 vs. 63.7 ± 11.9 mg/dL (NS) and 124.1 ± 9.4/75.8 ± 7.7 vs. 113.6 ± 9.6/65.8 ± 9.4 mmHg (systolic BP; NS, diastolic BP; p < 0.05), respectively. Both groups showed a significant reduction in the coronary plaque volume of -9.4 ± 10.7% and -8.7 ± 8.6% (NS) in standard and aggressive therapies, respectively. Both standard and aggressive intervention significantly regressed coronary plaque volume by the same degree, suggesting the importance of simultaneous reductions of LDL-C and BP for prevention of CAD.







 outcomes in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients aged 95 years and older: A nationwide population-based observational study
outcomes in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients aged 95 years and older: A nationwide population-based observational study



 ハーバード大学・Brigham and Women’s Hospitalへの留学
ハーバード大学・Brigham and Women’s Hospitalへの留学


















