 Emerin plays a crucial role in nuclear invagination and in the nuclear calcium transient
Emerin plays a crucial role in nuclear invagination and in the nuclear calcium transient
Shimojima M, Yuasa S, Motoda C, Yozu G, Nagai T, Ito S, Lachmann M, Kashimura S, Takei M, Kusumoto D, Kunitomi A, Hayashiji N, Seki T, Tohyama S, Hashimoto H, Kodaira M, Egashira T, Hayashi K, Nakanishi C, Sakata K, Yamagishi M, Fukuda K.
Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 14;7:44312. ![]()
Impact Factor (2016): 5.228![]()
Abstract
Alteration of the nuclear Ca2+transient is an early event in cardiac remodeling. Regulation of the nuclear Ca2+transient is partly independent of the cytosolic Ca2+transient in cardiomyocytes. One nuclear membrane protein, emerin, is encoded by EMD, and an EMD mutation causes Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD). It remains unclear whether emerin is involved in nuclear Ca2+ homeostasis. The aim of this study is to elucidate the role of emerin in rat cardiomyocytes by means of hypertrophic stimuli and in EDMD induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell-derived cardiomyocytes in terms of nuclear structure and the Ca2+transient. The cardiac hypertrophic stimuli increased the nuclear area, decreased nuclear invagination, and increased the half-decay time of the nuclear Ca2+transient in cardiomyocytes. Emd knockdown cardiomyocytes showed similar properties after hypertrophic stimuli. The EDMD-iPS cell-derived cardiomyocytes showed increased nuclear area, decreased nuclear invagination, and increased half-decay time of the nuclear Ca2+transient. An autopsied heart from a patient with EDMD also showed increased nuclear area and decreased nuclear invagination. These data suggest that Emerin plays a crucial role in nuclear structure and in the nuclear Ca2+transient. Thus, emerin and the nuclear Ca2+transient are possible therapeutic targets in heart failure and EDMD.
本論文の背景
Emery-Dreifuss型筋ジストロフィーは、X染色体劣性遺伝の疾患であり、核蛋白の1つであるエメリンの欠損により、近位筋の筋力低下、刺激伝導系の異常を伴う心筋障害、関節拘縮をきたす疾患です。核蛋白であるエメリンは、核膜の構造維持、核内転写因子の制御、クロマチンの構造維持に関わっているといわれています。また、心不全に至る過程において心筋細胞は、心筋自体に変化をきたす以前に核膜の陥入層の減少及び、核内カルシウム動態が変化し、核内カルシウム濃度が増加することが報告されていました(Circulation. 2014 Jul 15;130(3):244-55. ![]() )。そこで今回我々は、エメリンの欠損により、核の構造変化及び、核内カルシウム動態にどのような影響を及ぼすのかを検討しました。
)。そこで今回我々は、エメリンの欠損により、核の構造変化及び、核内カルシウム動態にどのような影響を及ぼすのかを検討しました。
要旨
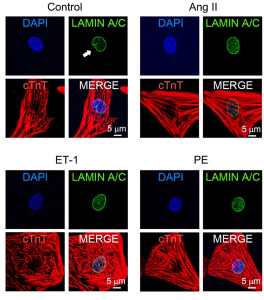
今回の解析には、ラット胎児心筋、Emery-Dreifuss型筋ジストロフィー患者由来のiPS細胞、剖検心筋を用いました。まずは、ラット胎児心筋に、心肥大のシグナルを亢進させるアンジオテンシンⅡ、エンドセリン、フェニレフリンを添加し、核膜陥入層の減少(図1)と核内カルシウム動態(50% decay timeの増大)の変化が見られました。
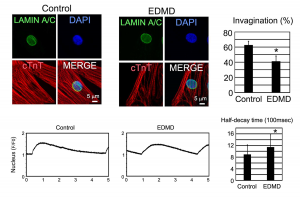
その後、Emery-Dreifuss型筋ジストロフィー患者由来のiPS細胞を用いて同様の実験を行ったところやはり核膜陥入層の減少と核内カルシウム動態の変化が認められました(図2)。最後にEmery-Dreifuss型筋ジストロフィー患者の剖検心筋組織を観察すると、核膜陥入層が有意に減少していました。
今後の展望
今回の研究でエメリンが核膜陥入層の形成と核内カルシウム動態に寄与し、この変化は、肥大シグナルを添加した時と同様の変化である可能性があることが示唆されました。今後、核内カルシウムの変化により発現が変化するといわれている転写因子のシグナル動態を検討することで、心不全やEmery-Dreifuss型筋ジストロフィーの新しい治療ターゲットを発見できる可能性があると考えてます。













